Understanding BigData: Its Characteristics, Challenges, and Benefits
In this tutorial, we will focus on what is big data, its characteristics, types, benefits, barriers, and job roles.
In this world of information, people are generating and consuming more-more data from each aspect of life. Human activities such as shopping, traveling, utility bills, banking operations, citizen, and government services are on electronic platforms. Organizations are moving from paper to digital platforms for most of the activities. These all activities generating tons of data every day. Organizations and governments utilize this data and generate some values using analytics for smooth operations and to gain competitive advantages. So in this century of information where data is playing a crucial role there, Big Data Analytics can be the game-changer for business.
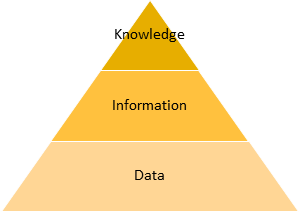
Data, Information, and Knowledge
Data is a number, word, or letter without Context or you can say it is a collection of raw facts. Information is a collection of data with the context or you can say it is process data. When we process the information we will identify hidden patterns and understand its implications then it will become knowledge. This knowledge has the real power of making crucial decisions in any government or private organization.
“Hiding within those mounds of data is the knowledge that could change the life of a patient, or change the world.” — Atul Butte, Stanford
Big Data
Big data is a large amount of data that cannot be handled by traditional IT systems. It has the capability to generate value for business and growth.
Big data is high-volume, high-velocity, and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation. — Gartner IT Glossary
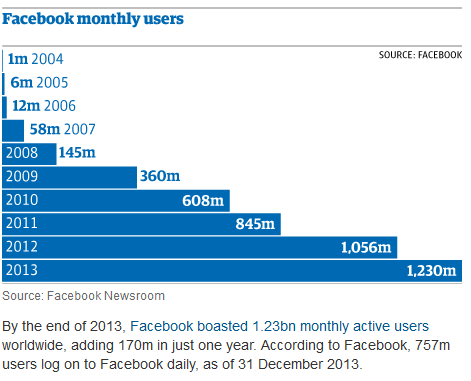
In 2020, Facebook has 4.5 billion users in the world.
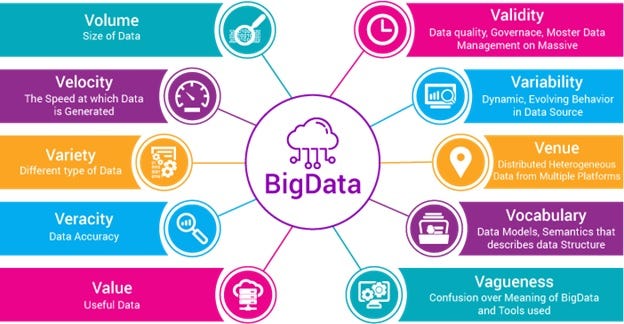
Characteristics
Here are the following characteristics:
- Volume (Data Quantity): Facebook and Google generate Peta Bytes of data every day.
- Velocity (Data Speed): Velocity is the rate of data production. if you see in the last decade we have exponentially generated the data.
- Variety (DataType): Variety means a type of data such as Text, Images, Videos, Audios, including log files.
Apart from these three core characteristics, we need to focus on 2 more characteristics: Validity and Value. Only large data will not enough we also need valid data and we can generate some values out of it. If we can’t generate any value then there is no point to accumulate and analyze it.
Another interesting view of the characteristics of Big Data can be seen in the following diagram:
An example
A fruit seller or any other small business that deals with one type of product, one market, and a single location. Such business does not need any Big data analytics but they do analyze their business by observing the customers. As per their own analysis and understanding of customers, he will offer the discount and according to quote the price.

If we talk about big stores such as Walmart, Costco, Aldi have multiple products, multiple markets, and multiple locations. They have millions of customers and millions of transactions each hour from various stores located around the world. This will generate a huge number of records per hour such data over the period of time will become big data due to volume, velocity, and variety. Such big organizations need big data solutions to understand customer needs, opinions, preferences, purchase habits, and sale trends.
Not only these retail stores, but other companies also have big data problems. Telecom companies such as Airtel having billions of calls each hour they need to store detail about each call. Financial companies such as Visa having millions of transactions each hour. Delivery service companies such as FedEx delivering and tracking millions of items across the world. Organizations that are generating millions of transitions per minute/hour facing the problem of Big Data.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is the process of exploring large data sets that contains a variety of data such as Tabular, Text, Image, Videos, Audios, etc. Here we uncover the hidden patterns, find correlations, trends, Identify potential customers and their business values, customer opinion and preferences, hiring top talents, and other business-related information.
Big data can be analyzed in two ways: Streaming and batch processing. In streaming, real-time data is processed and analyzed to provide quick and effective insights. In batch processing, data is stored and executed in batches for processing and analyzing to provide useful insights.
“Without big data analytics, companies are blind and deaf, wandering out onto the web like deer on a freeway.” — Geoffrey Moore, author and consultant
Benefits
- Discover accurate and impactful business insights.
- Targeted social media marketing.
- Real-time business operations.
- Identify business risks and threats.
- Understand customer opinions and sentiments.
- Analyze consumer before on each aspect of life.
- Business forecasting and planning
- Monitoring and tracking of applications
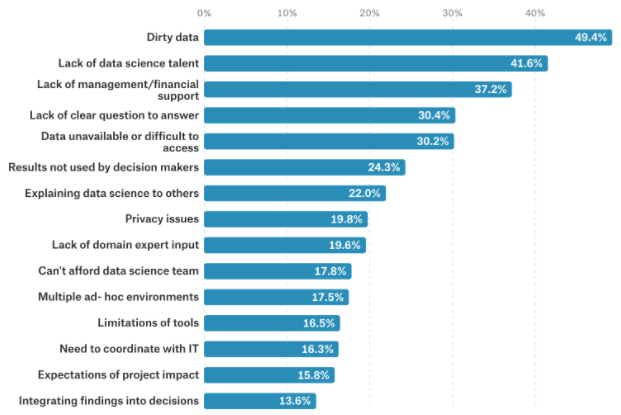
Challenges and Barriers
Big data is quite a new field. It’s mostly growth that happened in the last decade. Because of growth in data day by day, it puts lots of challenges and barriers for researchers and industry people. Let’s see those challenges and barriers:
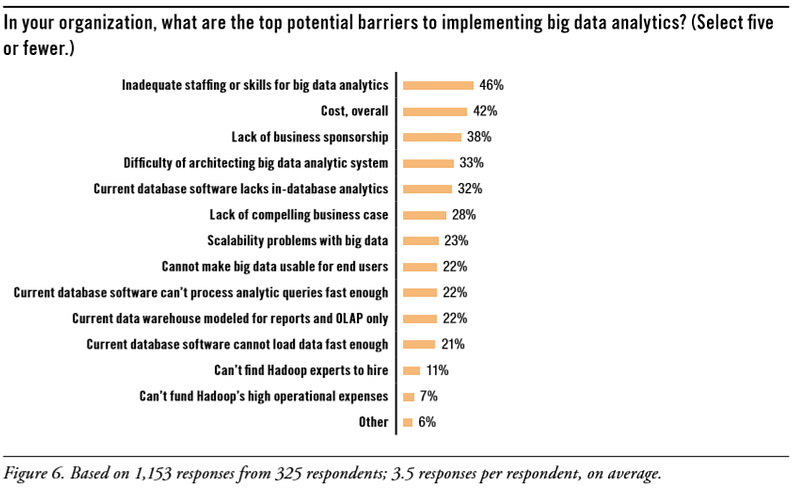
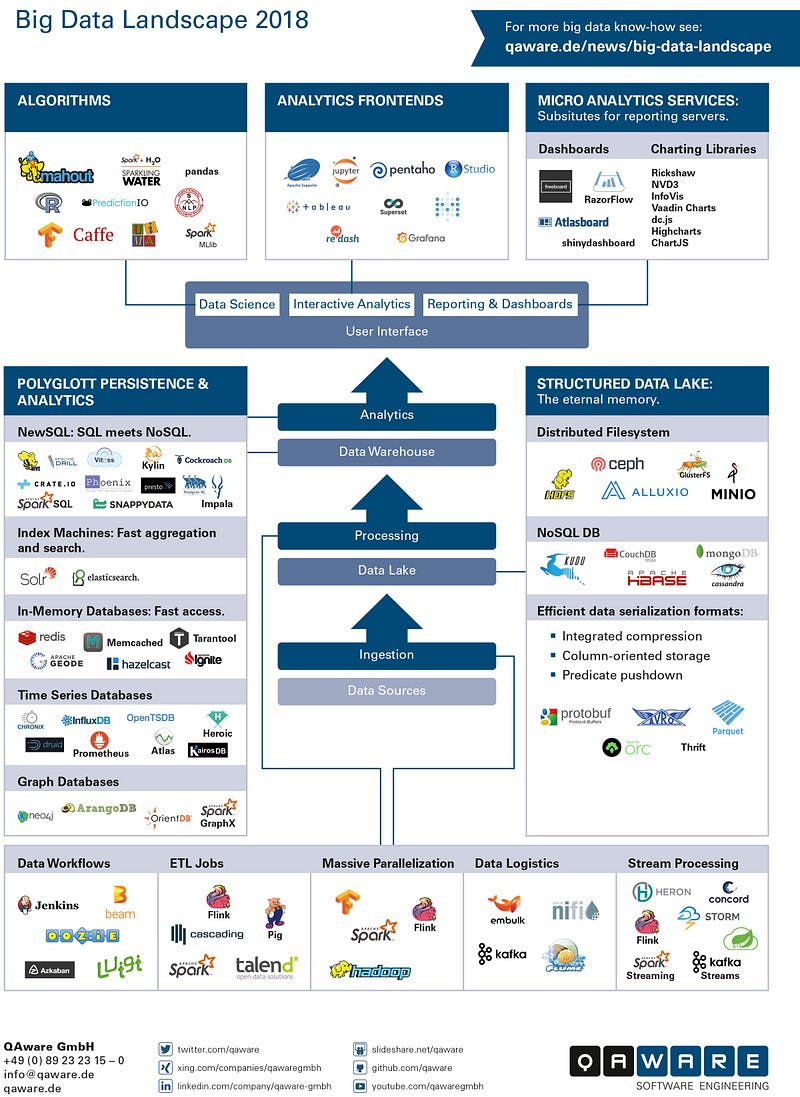
Big Data Landscape
Conclusion
The World’s most of the data is not structured i.e. it is unstructured type data. Most of the businesses and government organizations didn’t try to take advantage of it. Big data has the capability to generate more job opportunities and research challenges for industry and academia. The majority of the market is captured by Hadoop and Spark big data platforms for data processing and analysis.